Scaling the Future: 18 Open-Source Distributed Databases Every Dev Should Know
Explore 18 open-source distributed database solutions, understand what makes them essential for developers, and discover real-world use cases. Unlock scalability, resilience, and performance for your next project!
Table of Content
What’s a Distributed Database?
A distributed database is like the ultimate team player in the world of data storage. Instead of keeping all your data locked up in one place (like traditional databases), it spreads everything across multiple machines or nodes that work together as if they’re one system.
These nodes can be anywhere—different cities, countries, or even continents—but to you and your app, it feels like a single, seamless database. Cool, right?
This setup isn’t just about spreading data around; it’s about making your app faster, smarter, and more reliable. Think of it as having a bunch of backup dancers ready to step in if the lead performer trips.
Distributed databases are built to handle massive amounts of data, scale effortlessly, and keep your app running no matter what.
Why Should Developers Care About Distributed Databases?
As developers, we’re always looking for ways to make our apps better, faster, and more resilient. Here’s why distributed databases should be on your radar:
1. Scale Without Limits
Traditional databases hit a wall when traffic spikes or data grows too big. Distributed databases don’t care about walls—they scale horizontally. Need more power? Just add another node. No rewrites, no headaches. Perfect for apps that need room to grow.
2. Always-On Availability
Imagine your app going down during Black Friday sales or a major product launch. Nightmare, right? Distributed databases replicate data across nodes, so if one crashes, others pick up the slack. This means zero downtime, even during chaos.
3. Fail-Safe Fault Tolerance
Hardware fails, networks go down, and gremlins mess with servers—it’s life. Distributed databases laugh at these problems because they’re designed to survive failures. Data is replicated everywhere, so losing a node won’t lose your data.
4. Global Reach, Low Latency
Serving users worldwide? Distributed databases let you store data closer to them by deploying nodes in different regions. Faster queries = happier users. It’s like giving everyone a VIP ticket to your app.
5. Flexibility That Rocks
Whether you’re dealing with structured SQL data or unstructured JSON blobs, distributed databases adapt to your needs. Many also support cutting-edge features like real-time analytics, automatic sharding, and multi-model capabilities. Developer heaven!
When Do You Actually Use Distributed Databases?
Enough theory—let’s talk real-world scenarios where distributed databases shine:
1. E-Commerce Powerhouses
Picture an online store handling millions of orders daily. A distributed database keeps things running smoothly: inventory updates, payment processing, and shipping info—all lightning-fast and scalable. Plus, it handles flash sales without breaking a sweat.
2. Social Media Giants
Ever wonder how platforms like Instagram or TikTok stay snappy despite billions of posts and interactions? Distributed databases process this insane volume of data in real time, ensuring users see updates instantly, no matter where they are.
3. IoT Overlords
IoT devices generate insane amounts of sensor data—think smart homes, factories, or entire cities. Distributed databases process this locally and aggregate globally, enabling real-time insights for automation, monitoring, and decision-making.
4. Fintech Wizards
In finance, speed and accuracy are non-negotiable. Distributed databases power fraud detection, transaction processing, and risk analysis with ultra-low latency and rock-solid reliability. They’re the backbone of modern banking and fintech apps.
5. Gaming Legends
Multiplayer games demand split-second responses and crazy concurrency. Distributed databases track player stats, game states, and leaderboards across servers, ensuring a buttery-smooth experience for gamers worldwide.
6. Healthcare Heroes
Hospitals and telemedicine platforms rely on distributed databases to securely sync patient records, lab results, and medical histories across locations. Doctors get instant access to critical info, improving care and saving lives.
Why This Matters for You
Distributed databases aren’t just buzzwords—they’re tools that let you build apps capable of handling the chaos of today’s digital world. Whether you’re scaling a startup, launching a global platform, or building the next big thing, distributed databases give you the power to innovate fearlessly. So, next time you’re designing a system, think distributed. Your future self will thank you.
1- CockroachDB
CockroachDB is the ultimate cloud-native distributed SQL database that’s built to keep your data safe, available, and lightning-fast—no matter what.
It scales horizontally with ease, survives failures (from disk crashes to entire data-centers) without breaking a sweat, and ensures strong ACID compliance for rock-solid transactions.
With a familiar SQL API, it’s effortless to work with while delivering high availability and precise control over data placement. Perfect for modern apps that demand resilience and scale!
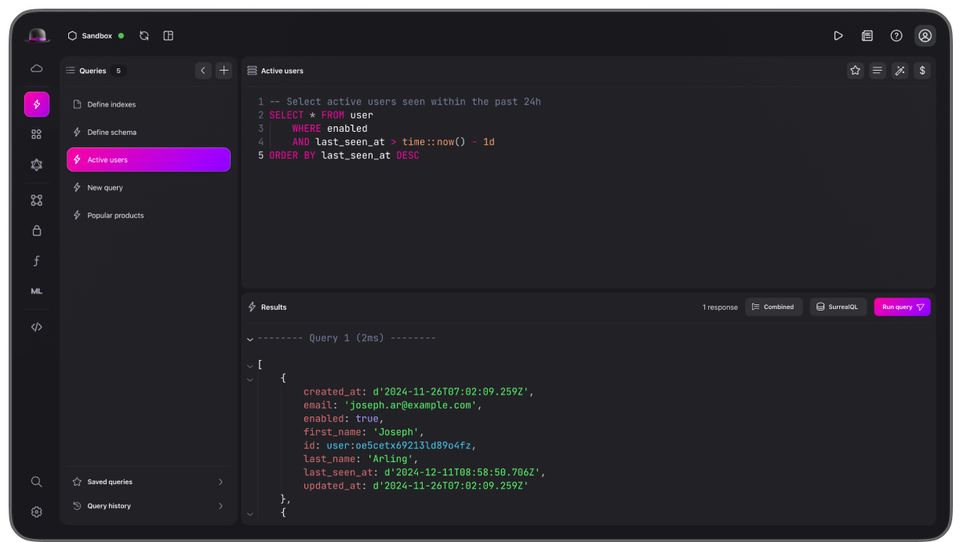
2- SurrealDB
SurrealDB is a cutting-edge, cloud-native database built for the realtime web. It combines the flexibility of a document-graph model with scalability and collaboration features, making it perfect for modern apps—whether you're working on web, mobile, or serverless projects.
By simplifying your database and API setup, SurrealDB helps you save time, reduce costs, and deliver secure, high-performance applications with ease.
SurrealDB is designed to be simple to install and simple to run - using just one command from your terminal. In addition to traditional installation, SurrealDB can be installed and run with HomeBrew, Docker, or using any other container orchestration tool such as Docker Compose, Docker Swarm, Rancher, or in Kubernetes.
Features
- Database server, or embedded library
- Multi-row, multi-table ACID transactions
- Single-node, or highly-scalable distributed mode
- Record links and directed typed graph connections
- Store structured and unstructured data
- Incrementally computed views for pre-computed advanced analytics
- Realtime-api layer, and security permissions built in
- Store and model data in any way with tables, documents, and graph
- Simple schema definition for frontend and backend development
- Connect and query directly from web-browsers and client devices
- Use embedded JavaScript functions for custom advanced functionality
3- etcd
etcd is a distributed, reliable key-value store designed for critical data in distributed systems, offering simplicity, speed, and resilience. With a user-friendly gRPC API, automatic TLS for security, and optional client authentication, it ensures safe and efficient data management.
It is built on the Raft consensus algorithm, etcd guarantees strong consistency and high availability, even during node failures. Benchmarked at 10,000 writes/sec, it powers mission-critical applications like Kubernetes, locksmith, and vulcand, making it a trusted choice for cloud-native and traditional systems alike.
4- TiDB
TiDB is a rock-solid, open-source distributed SQL database built for modern apps. It nails ACID compliance with distributed transactions, scales effortlessly (horizontally and vertically), and uses Raft consensus for high availability.
With strong consistency, automated failover, and geo-replication, it’s perfect for apps that demand reliability and performance at any scale.
Features
- Distributed Transactions : ACID compliance with a two-phase commit protocol for strong consistency across nodes.
- Scalability : Horizontal scaling by adding nodes; vertical scaling by upgrading resources—zero downtime.
- High Availability : Raft consensus ensures reliability, automated failover, and disaster tolerance with configurable geo-replication.
- HTAP (Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing) : Combines row-based (TiKV) and columnar (TiFlash) storage for real-time analytics and transactions.
- Cloud-Native : Deploy on Kubernetes (via TiDB Operator), public clouds, or on-premises; fully-managed option via TiDB Cloud.
- MySQL Compatibility : Works seamlessly with MySQL 8.0 protocols, tools, and frameworks; easy migration with minimal code changes.
- Open Source : Fully open under Apache 2.0 license, fostering transparency, innovation, and community collaboration.
5- FoundationDB
FoundationDB is a distributed database designed to handle large volumes of structured data across clusters of commodity servers. It organizes data as an ordered key-value store and employs ACID transactions for all operations.
It is especially well-suited for read/write workloads but also has excellent performance for write-intensive workloads. Users interact with the database using API language binding.
6- Citus
Citus is an open-source project that supercharges PostgreSQL by turning it into a distributed database, perfect for scaling performance. It shards tables across nodes for massive scalability, replicates reference tables for fast joins, and parallelizes queries cluster-wide.
With Citus, you get the power of distributed SQL without leaving the familiarity of PostgreSQL. 🚀
7- YugabyteDB
YugabyteDB is a PostgreSQL-compatible, high-performance, cloud-native, distributed SQL database. It combines the benefits of traditional relational databases with the scalability of NoSQL systems, making it suitable for applications that require both transactional consistency and the ability to handle large amounts of data.
It is best suited for cloud-native OLTP (that is, real-time, business-critical) applications that need absolute data correctness and require at least one of the following: scalability, high tolerance to failures, or globally-distributed deployments.
Features
- YSQL (Yugabyte SQL) : Reuses PostgreSQL query layer, supporting most features like datatypes, stored procedures, triggers, and extensions.
- YCQL (Yugabyte Cloud QL) : Semi-relational API with Apache Cassandra roots, supporting documents and indexing.
- Distributed Transactions : Google Spanner-inspired design with Raft consensus for strong consistency, ACID compliance, and support for snapshot, serializable, and read-committed isolation levels.
- Horizontal Scalability : Effortlessly scale IOPS and storage by adding nodes to the cluster.
- Continuous Availability : Native failover and repair with RPO=0 and RTO=~3 seconds for high resilience against failures.
- Geo-Distribution & Multi-Cloud : Deploy across zones, regions, or clouds; supports xCluster async replication (uni/bi-directional) and read replicas for low-latency stale reads.
- Multi-API Design : Extensible query layer supporting both relational (YSQL) and semi-relational (YCQL) APIs.
- 100% Open Source : Fully open under Apache 2.0 license, including enterprise-grade features like distributed backups, encryption, and change data capture.
- Resilience : Configurable to tolerate disk, rack, node, zone, region, and cloud failures automatically.
- Kubernetes-Native : Seamlessly deploy and manage YugabyteDB clusters in Kubernetes environments
8- CrateDB
CrateDB is a distributed SQL database that effortlessly handles massive data in real-time, blending the familiarity of SQL with NoSQL-like scalability. It’s built to ingest tens of thousands of records per second while running blazing-fast ad-hoc queries across the cluster.
CrateDB = Relational + NoSQL + Real-Time + Scalable—all in one sleek package. 🚀
Whether you’re working on a personal machine or a multi-region cloud setup, CrateDB scales horizontally with ease, thanks to its container-friendly, stateless architecture.
Query it using standard SQL via PostgreSQL wire protocol or an HTTP API, making it flexible for developers. Perfect for edge computing, analytics, and hybrid environments, CrateDB keeps things simple yet powerful.
Features
- SQL Power, No Limits: Query with standard SQL via PostgreSQL wire protocol or HTTP API—simple, flexible, and developer-friendly.
- Relational + Document Magic: Dynamic schemas and queryable objects bring document-oriented flexibility alongside rock-solid SQL capabilities.
- Time-Series & Search Superpowers: Built-in support for time-series data, real-time full-text search, and geospatial queries—perfect for analytics and location-based apps.
- Scale Like a Pro: Horizontally scalable clusters that thrive in virtualized and containerized environments (hello Kubernetes!).
- Blazing-Fast Queries: Distributed query execution so fast it feels like cheating.
- Zero Downtime, Always On: Auto-partitioning, sharding, and replication keep your data available, fault-tolerant, and self-healing.
- Smart Rebalancing: Automatically rebalances data when nodes join or leave—no manual babysitting required.
- Extend with UDFs: Add custom functionality using user-defined functions (UDFs) to make CrateDB truly yours.
9- rqlite
rqlite is a relational database which combines SQLite's simplicity with the power of a robust, fault-tolerant, distributed system. It's designed for easy deployment and lightweight operation, offering a developer-friendly and operator-centric solution for Linux, macOS, and Windows, as well as various CPU platforms.
rqlite Features
- Easy Deployment: Up and running in seconds—no separate SQLite installation required.
- Developer-Friendly: Simple HTTP API, CLI, and client libraries for seamless integration.
- Rich Feature Set: Full-text search, JSON support, and SQLite extensions like Vector Search and Crypto.
- Large Dataset Support: Handles multi-GB datasets with ease.
- Reliable: Fully replicated SQL database ensures fault-tolerance and high availability.
- Dynamic Clustering: Automatically integrates with Kubernetes, Consul, etcd, and DNS for clustering.
- Robust Security: Extensive encryption and TLS support for secure data management.
- Flexible Consistency: Customize read/write performance and durability to fit your needs.
- Scalable Reads: Read-only nodes for enhanced scalability and performance.
- Transactions: Supports a form of ACID-compliant transactions.
- Easy Backups: Hot backups with automatic support for AWS S3, MinIO, and direct SQLite restores.
10- NebulaGraph
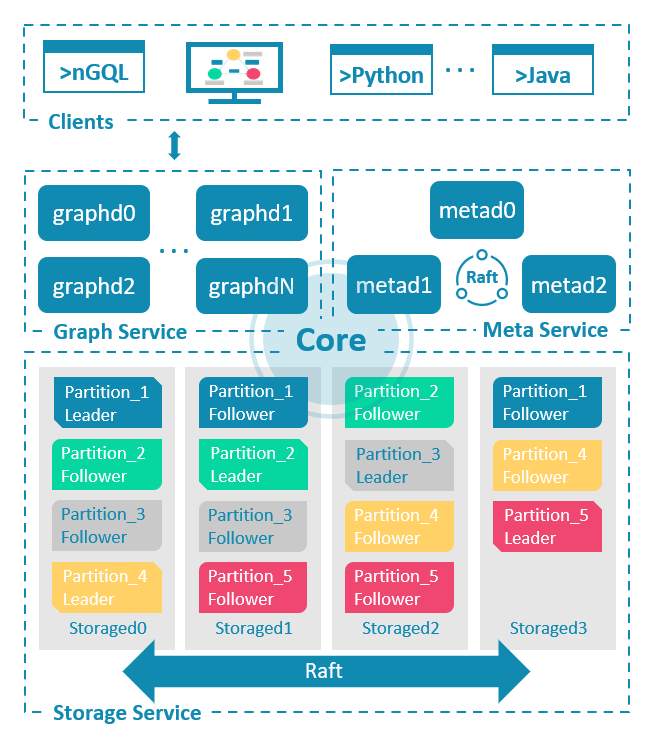
NebulaGraph is the go-to open-source graph database for developers who need speed, scale, and smarts. It crunches massive datasets with millisecond latency, scales effortlessly, and delivers lightning-fast graph analytics.
Whether you're building social media platforms, powering recommendation engines, mapping knowledge graphs, or tackling AI, security, or financial flows, NebulaGraph has your back.
Features
- Symmetrically distributed
- Storage and computing separation
- Horizontal scalability
- Strong data consistency by RAFT protocol
- OpenCypher-compatible query language
- Role-based access control for higher-level security
- Different types of graph analytics algorithms
11- CnosDB
HerdDB is a distributed SQL database that’s as fast as it is clever. Built for Java environments, it skips shared storage and uses Apache ZooKeeper and BookKeeper for rock-solid replication.
With a NoSQL core and an SQL layer powered by Apache Calcite, it’s perfect for high-speed writes and primary-key-heavy workloads.
Embeddable, transactional, and developer-friendly—HerdDB lets you bring your SQL skills to the distributed world.
12- HerdDB
HerdDB is a distributed SQL database that’s as fast as it is clever. Built for Java environments, it skips shared storage and uses Apache ZooKeeper and BookKeeper for rock-solid replication.
With a NoSQL core and an SQL layer powered by Apache Calcite, it’s perfect for high-speed writes and primary-key-heavy workloads. Embeddable, transactional, and developer-friendly—HerdDB lets you bring your SQL skills to the distributed world.
13- TiKV
Valkey is a high-performance, open-source key/value datastore that’s as versatile as it is fast. Whether you’re caching, managing message queues, or running it as a primary database, Valkey has you covered.
It supports standalone and clustered modes, with replication and high availability to keep your data safe and accessible.
TiKV Key Features
- Geo-Replication: Supports cross-region data replication using Raft and Placement Driver (PD).
- Horizontal Scalability: Scales effortlessly to 100+ TBs with PD and optimized Raft groups.
- Distributed Transactions: Guarantees externally-consistent ACID transactions, inspired by Google Spanner.
- Coprocessor Framework: Enables distributed computing, similar to HBase.
- Rust-Powered Consistency: Implements Raft consensus in Rust, ensuring strong data consistency with RocksDB storage.
- Auto-Sharding: PD enables automatic data migration and load balancing.
- Snapshot Isolation: Supports SI, SQL locks (SELECT ... FOR UPDATE), and consistent reads/writes.
- TiDB Integration: Optimized to work seamlessly with TiDB for HTAP workloads, RDBMS, and NoSQL patterns.
14- Presto
Presto is the ultimate SQL engine for querying massive datasets across data lakes, NoSQL databases, and more—all with sub-second performance. Built for speed and scale, it handles petabyte-sized analytics effortlessly, using ANSI SQL.
With an open-source, community-driven approach, Presto lets you query data where it lives, making it a developer’s secret weapon for fast, flexible insights.
15- Valkey
Valkey is a high-performance, open-source key/value datastore that’s as versatile as it is fast. Whether you’re caching, managing message queues, or running it as a primary database, Valkey has you covered. It supports standalone and clustered modes, with replication and high availability to keep your data safe and accessible.
It is packed with rich datatypes like hashes, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, and hyperloglogs, it lets you manipulate data in-place using powerful commands. Plus, Lua scripting and module plugins make it endlessly extensible.
16- GreptimeDB
GreptimeDB is the ultimate open-source, cloud-native time series database that brings metrics, logs, and events together under one roof. Built for scalability, it decouples compute and storage, making it a perfect fit for edge deployments or distributed clusters in Kubernetes.
With Rust-powered performance, it’s blazing fast, cost-efficient (50x on cloud storage!), and supports SQL, PromQL, and more. Plus, its interoperability with tools like Prometheus and Elasticsearch makes migration a breeze.
17- Dgraph
Dgraph is a distributed GraphQL database built for scalability and performance, offering ACID transactions, consistent replication, and linearizable reads. Designed from scratch for rich queries, it optimizes data storage on disk to minimize disk seeks and network calls, ensuring high throughput and low latency.
As a native GraphQL database, it supports real-time queries over terabytes of data, responding in JSON or Protocol Buffers via GRPC/HTTP.
18- KeyDB
KeyDB is a fast fully open-source, high-performance database and a faster drop-in alternative to Redis. Backed by Snap, it offers features like multi-threading, enhanced scalability, and compatibility with Redis APIs.
Features
- High Throughput : Multithreaded design handles over 1M ops/sec per node, outperforming Redis.
- Low Latency : Submillisecond response times with in-memory data storage.
- Rich Data Structures : Strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, geospatial indexes, and streams.
- Multiple Persistence : Configurable RDB snapshots and AOF for durability.
- Scalability : Scale vertically or horizontally via active-replication, cluster-mode, or sharding.
- High Availability : Active-replica nodes with automatic failover; no sentinel nodes required.
- MVCC Non-Blocking : Avoid blocking calls like SCAN/KEYS with concurrent snapshot queries.
- Cross-Region Multi-Master : Asynchronous replication with last-write-wins for multi-master setups.
- Better EXPIREs : Subkey expiration and near real-time active deletion.
- TLS Encryption : 7x faster than Redis + TLS, with multithreading to maintain performance.
- ModJS : Open-source JavaScript module for custom commands using the V8 engine.
- Upcoming Features : FLASH storage, JSON support, multi-tenancy, and RAFT.