From Prototypes to Production: 6 Free MongoDB Frameworks You Can’t Ignore!
Table of Content
As, MongoDB has become one of the most popular NoSQL databases, thanks to its flexibility, scalability, and developer-friendly design. But what makes MongoDB even more powerful is its seamless integration with a variety of frameworks and tools that simplify development, enhance performance, and enable real-time capabilities.
Whether you're building web applications, mobile apps, or complex data pipelines, MongoDB’s ecosystem supports a wide range of frameworks to suit your needs.
MongoDB is widely used across industries for applications requiring real-time data processing, high performance, and seamless scalability. Whether you're building chat applications, real-time analytics platforms, or gaming backends, MongoDB provides the tools needed to manage and scale your data effectively.

Key Features of MongoDB
- Schema-Free NoSQL :
MongoDB's document-based structure eliminates the need for rigid schemas, enabling dynamic and flexible data modeling. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where data structures evolve over time. - Super Easy to Use :
With a developer-friendly API and intuitive query language, MongoDB simplifies database interactions. Its JSON-like BSON format ensures that working with data feels natural for modern developers. - Real-Time Capabilities :
MongoDB supports real-time data ingestion and querying, making it suitable for applications that require instant updates, such as chat apps or live dashboards. - Replication and High Availability :
MongoDB offers built-in replication (via replica sets) to ensure data durability and fault tolerance. - Local MiniMongo and Sync :
MongoDB provides lightweight local storage options like MiniMongo, which is often used in client-side applications. It also supports synchronization between local and remote databases for offline-first applications. You can check Meteor's MiniMongo that works completely offline as using the browser. - Scalability : Horizontal scaling through sharding allows MongoDB to handle massive datasets and high traffic loads.
- Indexing : Supports secondary indexes for faster query performance, and fast search.
- Aggregation Framework : A powerful tool for performing complex data transformations and analytics.
- Security : Role-based access control, encryption, and compliance with major regulatory standards.
- Cloud Integration : Fully managed cloud offerings via MongoDB Atlas , providing automated backups, monitoring, and global distribution.

When Should You Use MongoDB?
MongoDB is a powerful database solution that truly stands out in scenarios where flexibility, scalability, and real-time performance are essential. Its ability to handle diverse data types and adapt to evolving requirements makes it a top choice for a variety of applications.
In the following some use-cases on which apps you can build using MongoDB:
1. Chat Applications
If you’re building a chat app or any application that requires real-time communication, MongoDB is an excellent fit. Its real-time capabilities allow for instant message delivery and seamless synchronization across multiple devices.
2. Real-Time Applications
From stock trading platforms to IoT (Internet of Things) systems, MongoDB excels in environments where data needs to be processed and served in real time. For example, financial applications that require up-to-the-second updates on stock prices or IoT systems that collect and analyze sensor data benefit greatly from MongoDB’s speed and scalability.
Its ability to handle high-throughput workloads makes it ideal for these demanding use cases.
3. Monitoring Systems
When it comes to monitoring server logs, application metrics, or network performance, MongoDB is a natural choice. It can efficiently handle large volumes of time-series data—data that is collected over time at consistent intervals.
This makes it perfect for tracking trends, detecting anomalies, and generating insights from continuous streams of information. Whether you’re monitoring cloud infrastructure or analyzing application health, MongoDB provides the tools you need to stay ahead.
4. Gaming Backends
The gaming industry generates massive amounts of unstructured data, from player profiles and leaderboards to in-game events and transaction histories. MongoDB’s schema-free design allows developers to store this diverse data without worrying about rigid structures or complex migrations.
Additionally, its scalability ensures that gaming backends can handle millions of users and their interactions seamlessly. Whether you’re building casual mobile games or large-scale multiplayer experiences, MongoDB has you covered.
If your project involves dynamic, unstructured, or rapidly growing data, MongoDB is likely the right tool for the job. Its versatility and robust ecosystem make it a go-to solution for modern applications across industries.
Now, Let’s dive into some of the key frameworks and tools that work hand-in-hand with MongoDB, making it a go-to choice for developers worldwide.
Open-source MongoDB Frameworks
1- Joystick (New Generation Full-stack Hero, That I DO NOT Like)
Joystick is an open-source full-stack app development framework for building real-time apps, it supports MongoDB and PostgreSQL by default, enables developers to create a scalable full-stack structured app easily.
It is fast, comes with a real-time HMR development server that supports instant updates, and supports fast app builds.
While I was Meteor users for years, I do not have much love for Joystick, yet Joystick seems promising for building enterprise apps, yet its community is small.
2- Meteor

Oh, where to start? I began using Meteor back in 2013, and over the years, I’ve completed several projects—both personal and for clients. It’s an ideal platform for building enterprise-grade real-time applications. I’ve used it to create games, for web scraping, various data-driven projects, offline apps (utilizing only MiniMongo), tiny games for my kid, and even an industrial automation project for a customer.
Meteor is a cool platform, not just a framework, as it allows developers to use their favorite frameworks within it: React, Solid.js, Vue, Svelte, Angular, and Blaze.js. It also comes with a fast real-time development server and uses DDP (Distributed Data Protocol), which leverages an in-browser database via MiniMongo.
3- MEAN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js)

The MEAN stack is a widely-used, open-source framework for building dynamic and scalable web applications. It combines four key technologies—MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, and Node.js—into a cohesive, JavaScript-based solution. MongoDB, a NoSQL database, stores data in flexible JSON-like documents, making it perfect for handling unstructured or evolving data. Express.js simplifies server-side development by providing tools for creating APIs and managing HTTP requests efficiently.
Angular, maintained by Google, powers the front end, enabling developers to build interactive single-page applications (SPAs) with features like two-way data binding and reusable components. Node.js runs JavaScript on the server side, using an event-driven, non-blocking architecture that ensures high performance and scalability.
One of the biggest advantages of the MEAN stack is its use of JavaScript throughout the entire application, from the database to the frontend. This eliminates the need to switch between languages, streamlining development and improving productivity.
The stack is also ideal for real-time applications, such as chat systems or live dashboards, thanks to Node.js’s efficiency and Angular’s responsiveness.

4- MERN Stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, Node.js)
The MERN stack—composed of MongoDB, Express.js, React.js, and Node.js—has been a transformative tool in my development journey. Its seamless use of JavaScript across the entire stack, from database to frontend, has streamlined my workflow and allowed me to focus on solving real challenges without the hassle of switching languages or frameworks.
Over the years, I’ve used the MERN stack for a variety of projects, both personal and client-based, ranging from real-time chat applications and data dashboards to small games and industrial automation systems.
One notable project was a small e-commerce platform where the MERN stack truly shone. MongoDB efficiently managed product data, user reviews, and order histories, while React.js enabled a dynamic, single-page interface that let users browse, add items to their cart, and checkout without page reloads.
Express.js simplified API creation, ensuring smooth communication between the frontend and backend. The stack’s flexibility, scalability, and real-time capabilities made it an ideal choice for this project, and it reinforced my appreciation for how powerful and versatile the MERN stack can be.
5- KeystoneJS
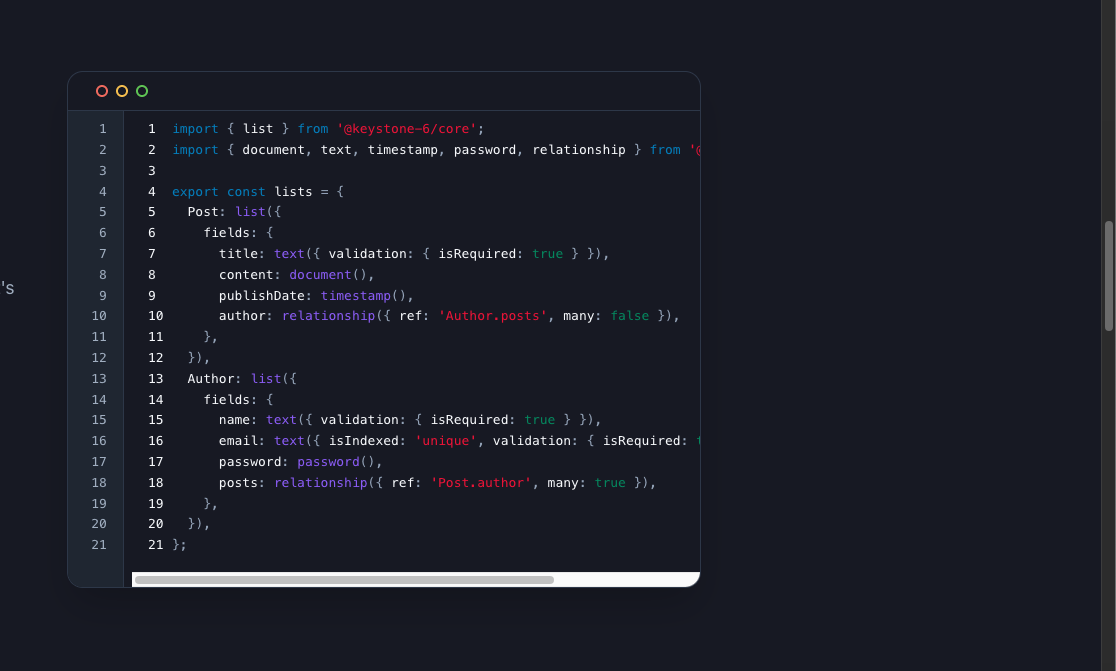
Keystone is an open-source headless CMS that can be used o build quick backend over MongoDB that enables developers to write their own frontend over any library of their choice such as React, React Native, Svelte, Vue, Angular, Next.js, Solid.js and others.
I’ve been using Keystone CMS for a while now, and it’s become my go-to for building backends that are both powerful and flexible. What I love most is how it works seamlessly with MongoDB , giving me the freedom to design schemas that adapt as projects grow. As a developer, I can describe my data models in code, and Keystone automatically generates a GraphQL API —no boilerplate, no headaches. It’s clean, intuitive, and saves so much time.
One of my favorite projects was building a custom e-commerce platform. Keystone’s headless CMS architecture let me integrate it effortlessly with a React frontend while managing product catalogs, user roles, and orders through MongoDB. The access control features were a lifesaver, ensuring secure, role-based permissions without extra complexity. Moreover, tools like rich text editing and relational data handling made content management smooth for non-technical users.
Keystone strikes the perfect balance between simplicity and power. Whether you’re building a blog, an app, or even something experimental, it’s a joy to work with—a true developer’s CMS.
It is ideal as a backend system for mobile apps, content heavy websites, IoT apps, eCommerce websites.

6- Deployd
Although it hasn’t been updated in years, Deployd remains a tool that allows developers to quickly build secure backend APIs on top of MongoDB . However, as mentioned, it lacks many of the enterprise-grade features found in modern platforms like Keystone , Meteor , or others.
Unlike Meteor , which supports WebSockets , REST APIs , and GraphQL , Deployd focuses solely on building REST APIs . While it can still be useful for prototyping over MongoDB, we strongly advise against using it in production environments due to its outdated nature and limited functionality.
For modern projects, especially those requiring scalability and advanced features, tools like Keystone or Meteor are far more robust and future-proof. Use Deployd only if you’re experimenting or need a quick proof of concept—but don’t rely on it for serious, long-term development.
Which one to use?
1- For Enterprise Grade apps that scale:
- Joystick
- Meteor
2- Content Heavy Project
- Keystone
3- Prototyping and proof-of-concept
- Meteor: It is good for quick MVP, supports offline in-browser data.
- Deployd (not recommended for production)
- Keystone (heavy but get the things done)
4- Games
- Meteor: Reactive, Fast, Real-time, works with all libraries
5- eCommerce Systems
- KeystoneJS
Final Note
Choosing the right database is critical to the success of any application, and MongoDB proves itself time and again in scenarios where traditional databases fall short. Whether you’re building chat apps, real-time analytics platforms, monitoring tools, or gaming backends, MongoDB’s flexibility, scalability, and real-time capabilities ensure that your application performs optimally under pressure.
So, if you’re looking for a database that can grow with your project and adapt to your evolving needs, MongoDB might just be the perfect match.